
Copper Wire
Properties of Copper Wire
- High Electrical Conductivity: Efficiently transmits electrical currents.
- Ductility and Malleability: Easily bent and shaped without breaking.
- Corrosion Resistance: Forms a protective oxide layer.
- Thermal Conductivity: Transfers heat effectively.
Types of Copper Wire
- Bare Copper Wire: Uncoated and used for grounding or transmission.
- Tinned Copper Wire: Coated with tin for corrosion resistance.
- Stranded Copper Wire: Multiple strands twisted together for flexibility.
- Solid Copper Wire: Single solid conductor used in permanent installations.
Applications of Copper Wire
- Electrical wiring in homes, buildings, and industries
- Power generation and distribution
- Electronics and telecommunication systems
- Automotive wiring and components
- Renewable energy systems like solar panels and wind turbines
Specifications of Copper Wire
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Material | 99.9% Pure Copper |
| Conductivity | 58.0 MS/m (at 20°C) |
| Melting Point | 1,085°C (1,984°F) |
| Density | 8.96 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 210 MPa (for annealed copper) |
Features of Copper Wire
- Flexibility: Easily bent and installed in complex electrical systems.
- Durability: Resistant to mechanical wear and tear.
- Low Resistance: Ensures minimal energy loss during transmission.
- Heat Resistance: Maintains performance at high temperatures.
- Recyclable: Environmentally friendly and 100% recyclable.
Copper Wire Size Chart
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Diameter (mm) | Cross-Sectional Area (mm²) | Current Capacity (Amps) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2.59 | 5.26 | 30 |
| 12 | 2.05 | 3.31 | 20 |
| 14 | 1.63 | 2.08 | 15 |
| 16 | 1.29 | 1.31 | 10 |
| 18 | 1.02 | 0.823 | 7 |
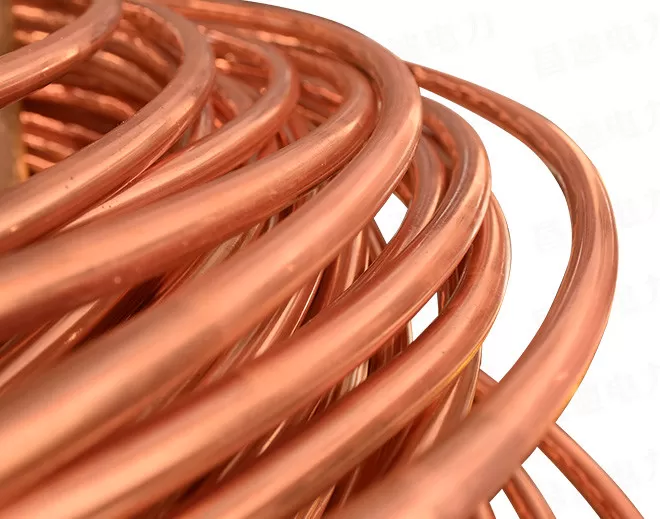
Tinned Copper Wire
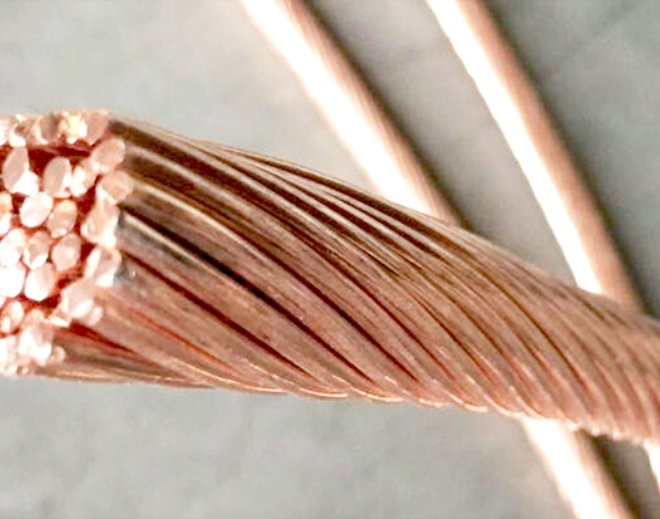
Stranded Copper Wire

Bare Copper Wire
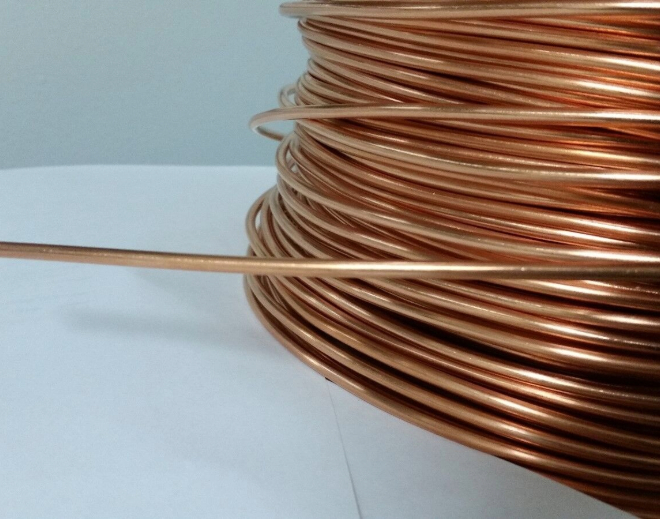
Solid Copper Wire
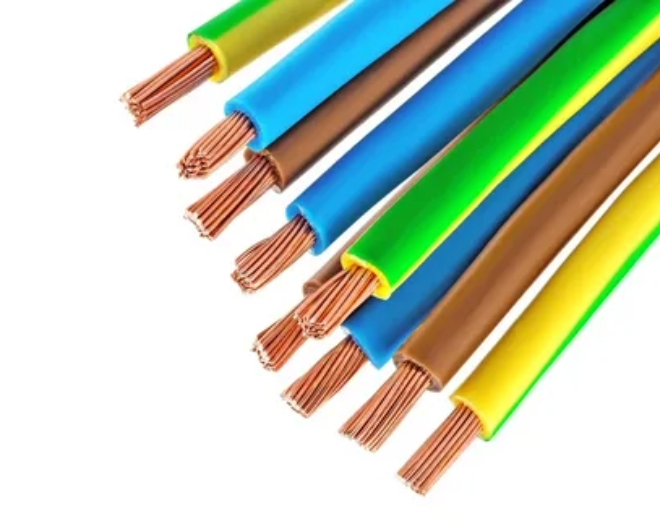
Insulated Copper Wire

Coaxial Copper Wire
